Learn how to encode videos using Laravel and FFmpeg. A step-by-step guide covering queues, storage, and performance for real-world video platforms.
Laravel + FFmpeg: Encoding Videos Step by Step
Uploading a video is easy. Encoding it efficiently, reliably, and at scale is not.
If you are building a video platform with Laravel, video encoding is one of the most critical technical challenges you’ll face. This guide walks through a practical, production-oriented approach to encoding videos using Laravel and FFmpeg.
Why FFmpeg Is the Standard
FFmpeg is widely used because it offers:
-
Full control over video formats
-
Support for multiple resolutions
-
Excellent performance
-
No vendor lock-in
Combined with Laravel’s queue system, FFmpeg becomes a powerful tool for video processing.
The Core Architecture
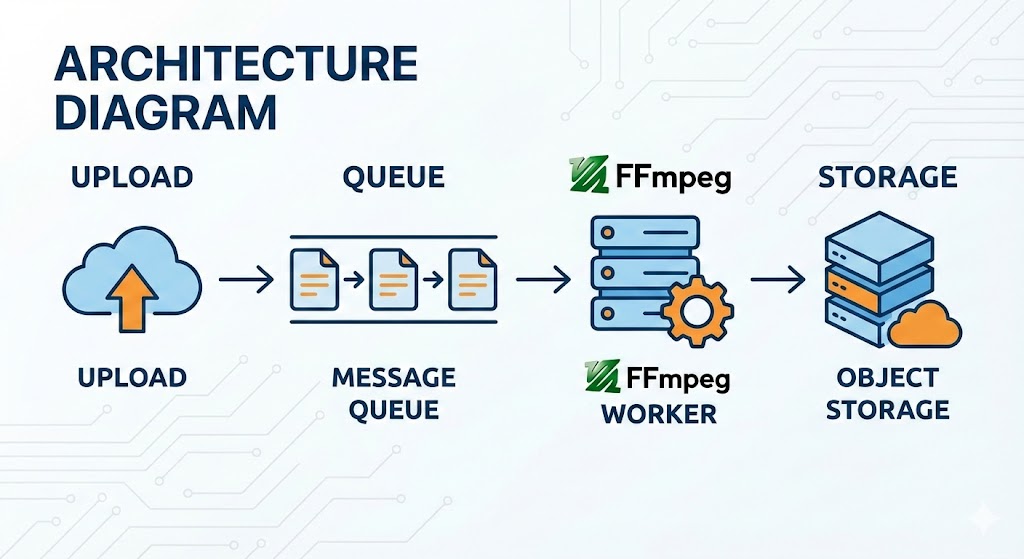
A scalable video encoding flow usually looks like this:
-
User uploads a video
-
File is stored temporarily
-
A Laravel job is dispatched
-
FFmpeg processes the video
-
Encoded files are stored
-
Video status is updated
This approach keeps your application responsive while heavy processing happens in the background.
Step-by-Step Encoding Flow
1. Upload and Store
The uploaded video is saved to temporary storage. This keeps the request fast and avoids timeouts.
2. Dispatch a Queue Job
Laravel queues allow you to move encoding work out of the request lifecycle. Each video encoding task runs independently.
3. Run FFmpeg
FFmpeg converts the original file into the required formats and resolutions. You can generate multiple outputs if needed.
4. Store the Result
Encoded videos are uploaded to external storage such as S3-compatible services.
5. Update Status
Once encoding finishes, the video is marked as ready and becomes available to users.
Scaling the System
To handle growth, you can:
-
Add more queue workers
-
Separate encoding servers
-
Use external object storage
-
Monitor job performance
This modular design allows the system to scale without rewriting the core application.
Real-World Implementation
This architecture is used in 89vids, a production-ready Laravel video platform.
Instead of building this pipeline from scratch, many developers prefer starting with a system that already handles encoding, queues, and storage reliably.
Conclusion
Laravel and FFmpeg are a powerful combination when used correctly. By separating uploads, processing, and delivery, you can build a video platform that scales with confidence.
Published on February 07, 2026
Others Posts

Alternatives to Cameo: Build Your Own Personalized Celebrity Video Platform
February 07, 2026Looking for alternatives to Cameo? Discover the best options for creat...
Read more
How I Built a Video Platform with Laravel: The Architecture Behind 89vids
February 07, 2026A behind-the-scenes look at how a scalable video platform was built us...
Read more